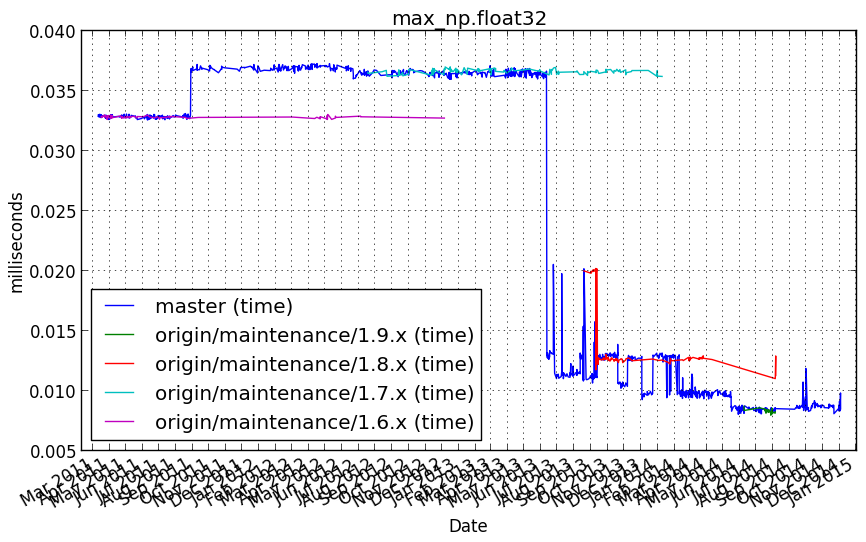
vb_reduce¶
max_np.float32¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(20000, dtype=np.float32)
Benchmark statement
np.max(d)
Performance graph
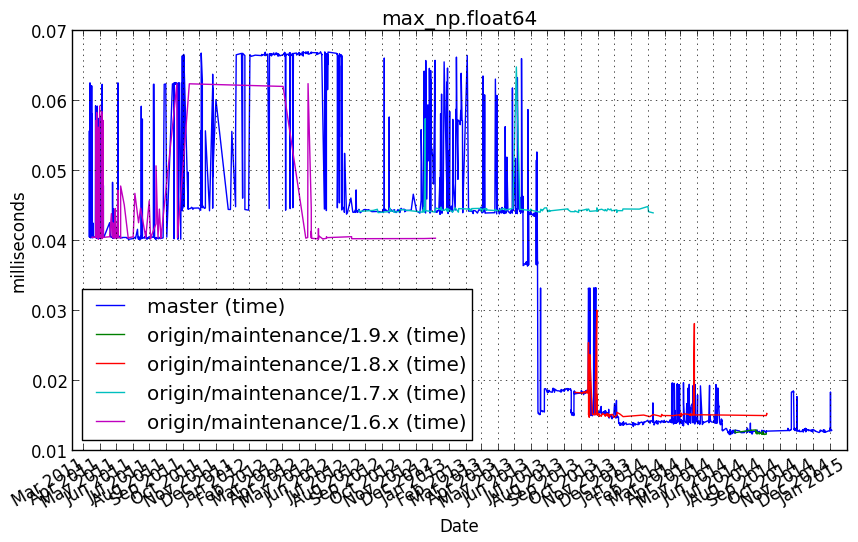
max_np.float64¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(20000, dtype=np.float64)
Benchmark statement
np.max(d)
Performance graph
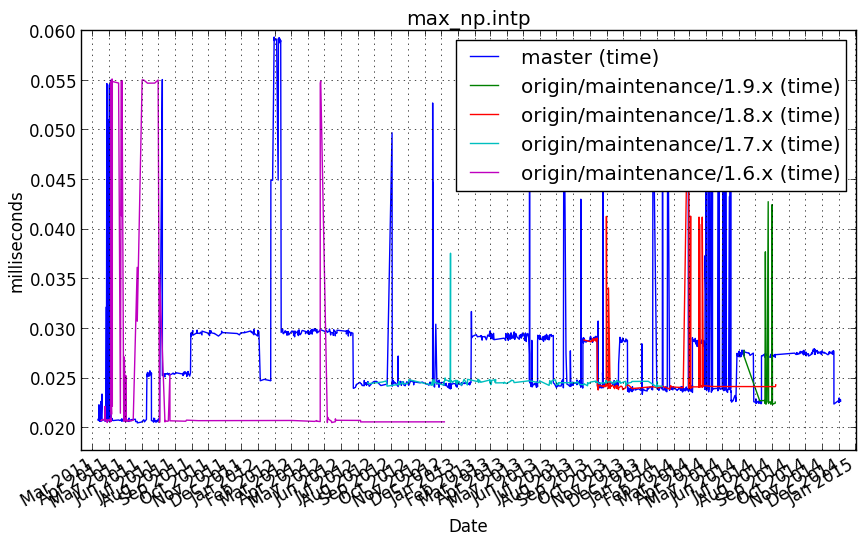
max_np.intp¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(20000, dtype=np.intp)
Benchmark statement
np.max(d)
Performance graph
min_np.float32¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(20000, dtype=np.float32)
Benchmark statement
np.min(d)
Performance graph
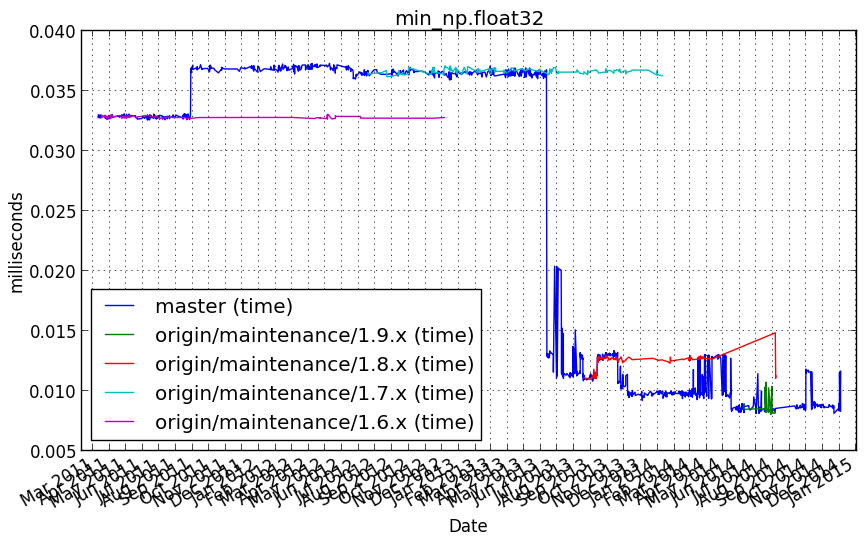
min_np.float64¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(20000, dtype=np.float64)
Benchmark statement
np.min(d)
Performance graph
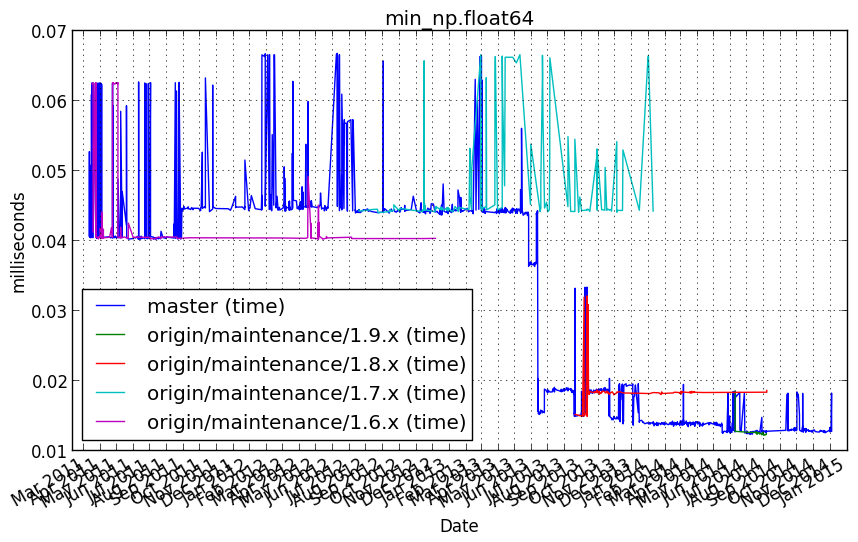
min_np.intp¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(20000, dtype=np.intp)
Benchmark statement
np.min(d)
Performance graph
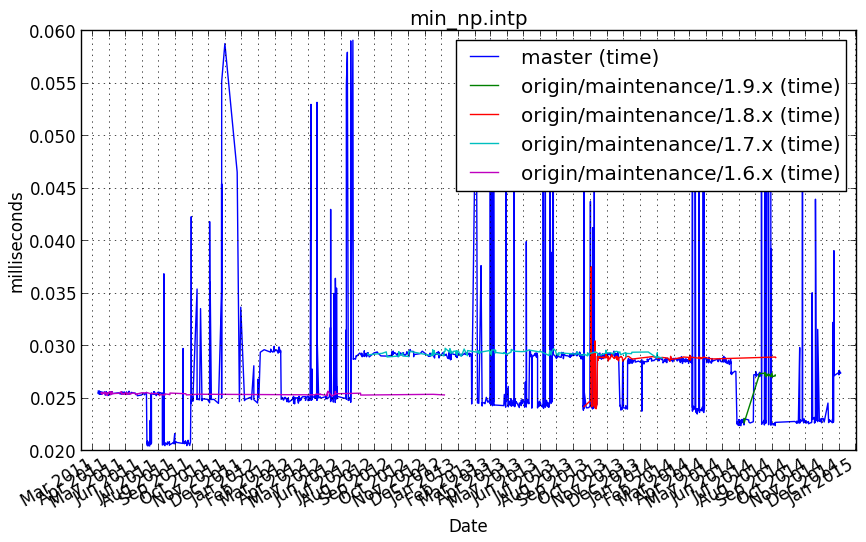
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
Benchmark statement
[numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0) for a in squares.itervalues()]
Performance graph
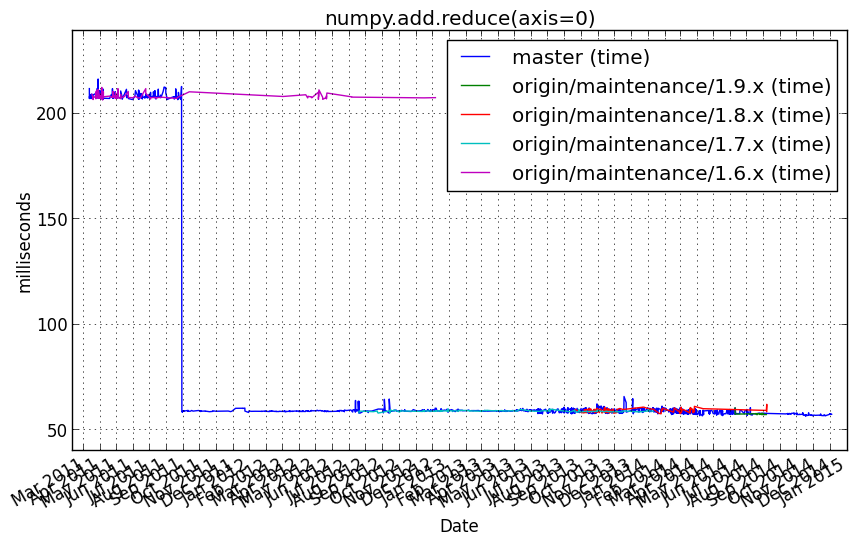
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_complex128¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['complex128']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
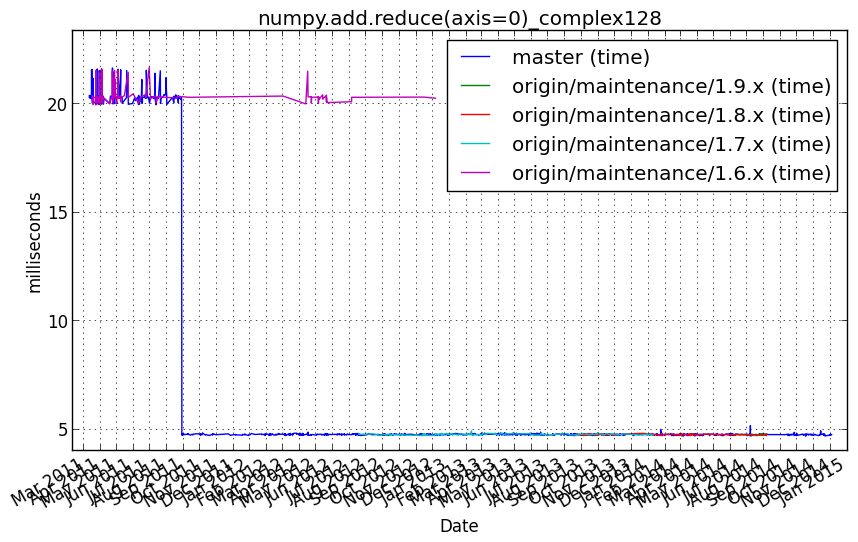
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_complex256¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['complex256']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
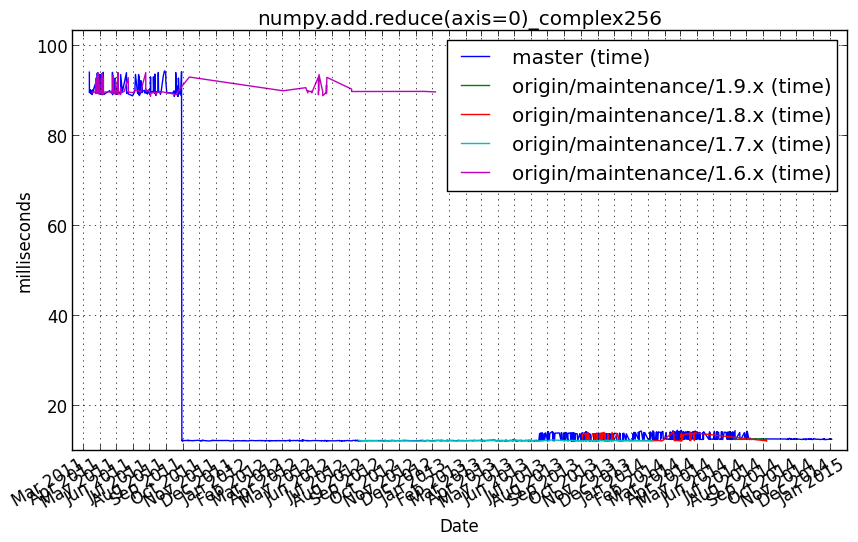
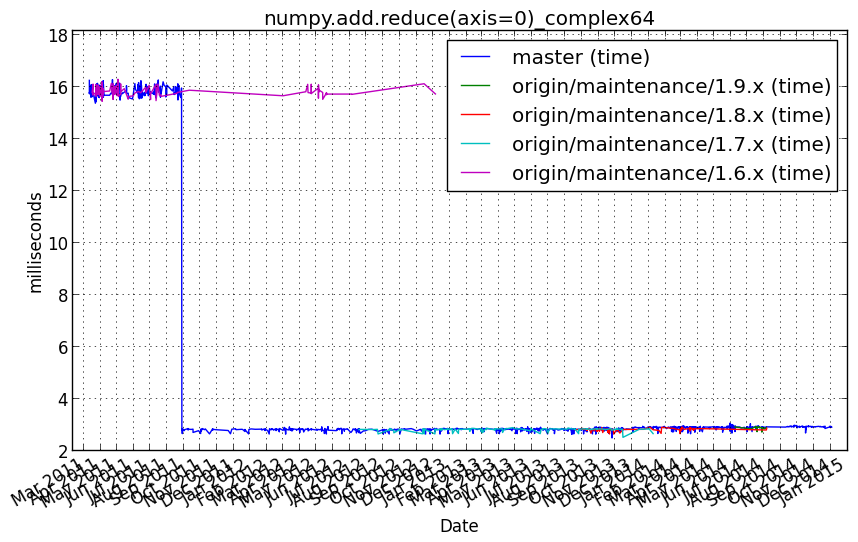
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_complex64¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['complex64']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
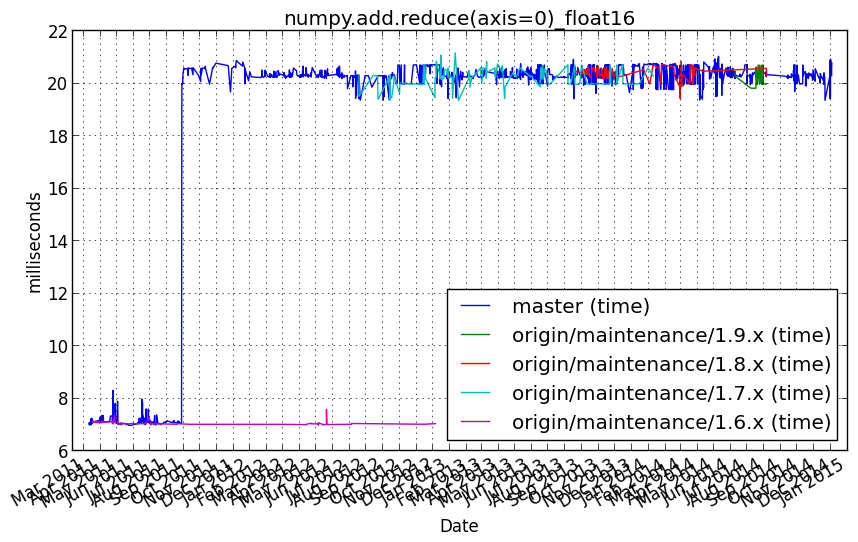
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_float16¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['float16']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_float32¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['float32']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
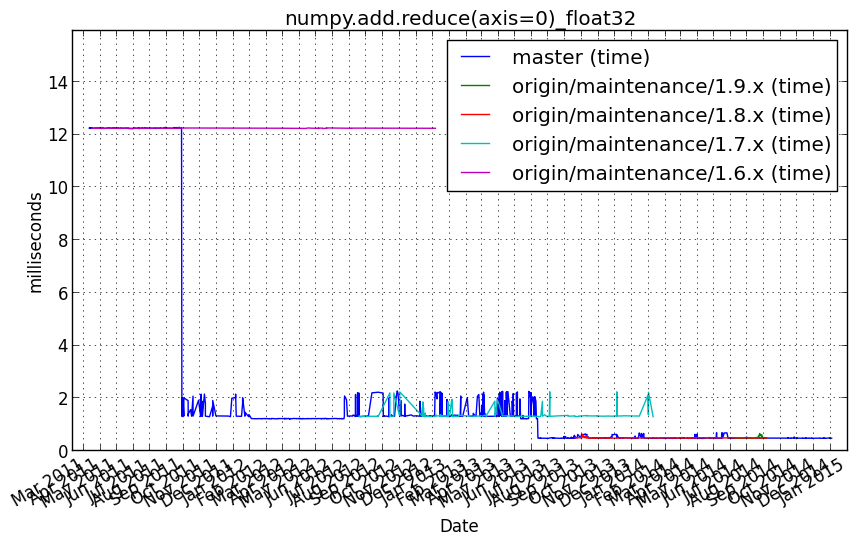
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_float64¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['float64']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
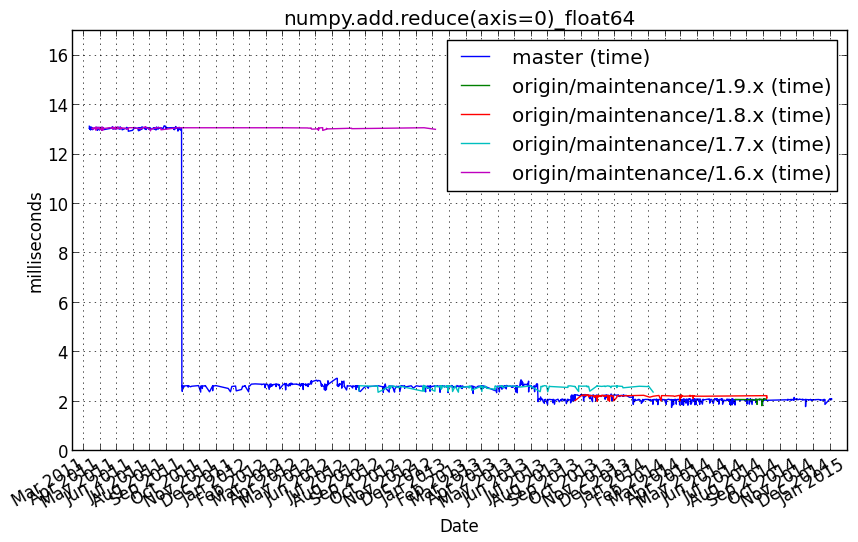
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_int16¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['int16']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
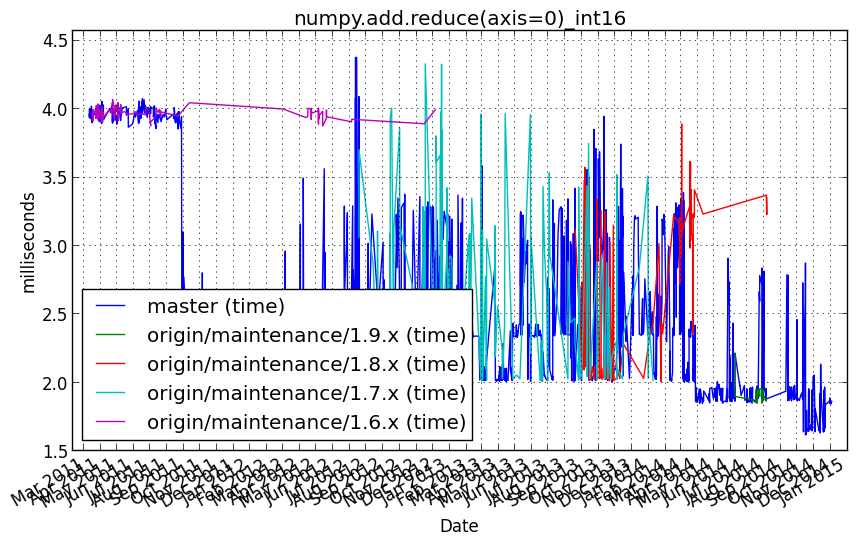
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_int32¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['int32']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
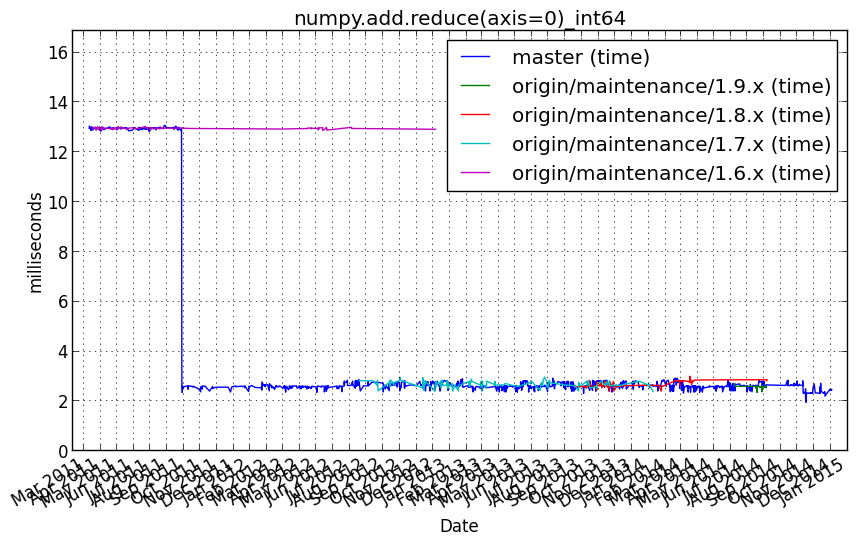
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_int64¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['int64']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
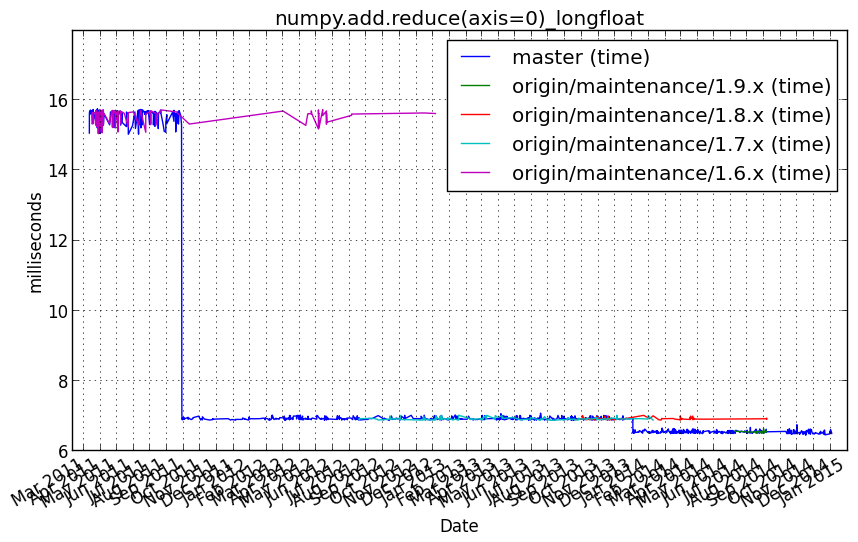
numpy.add.reduce(axis=0)_longfloat¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['longfloat']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=0)
Performance graph
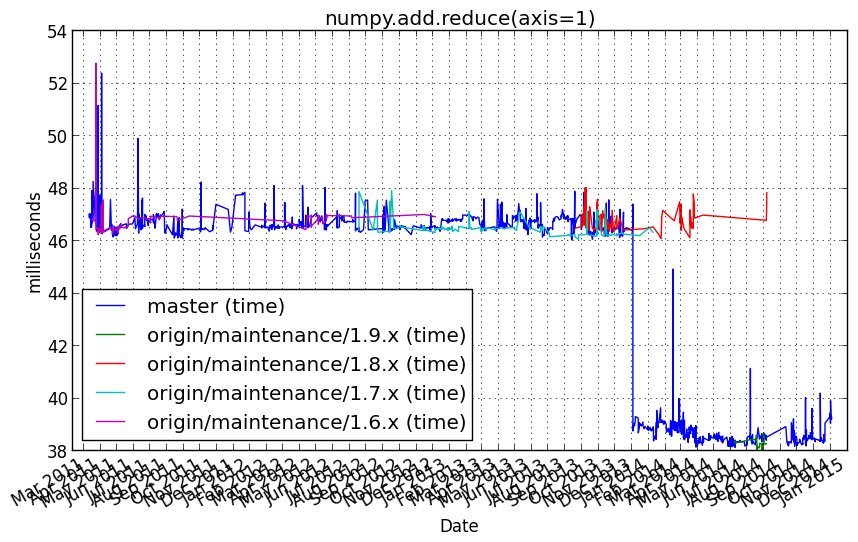
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
Benchmark statement
[numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1) for a in squares.itervalues()]
Performance graph
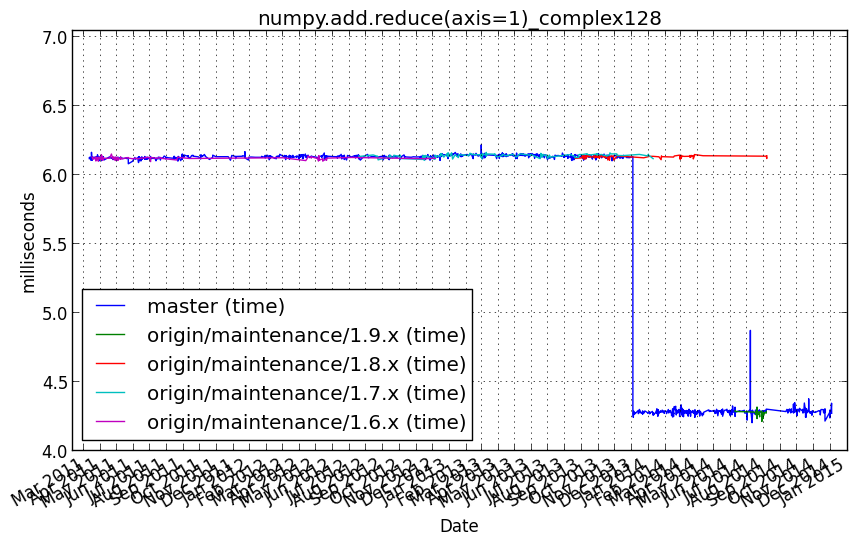
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_complex128¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['complex128']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_complex256¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['complex256']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
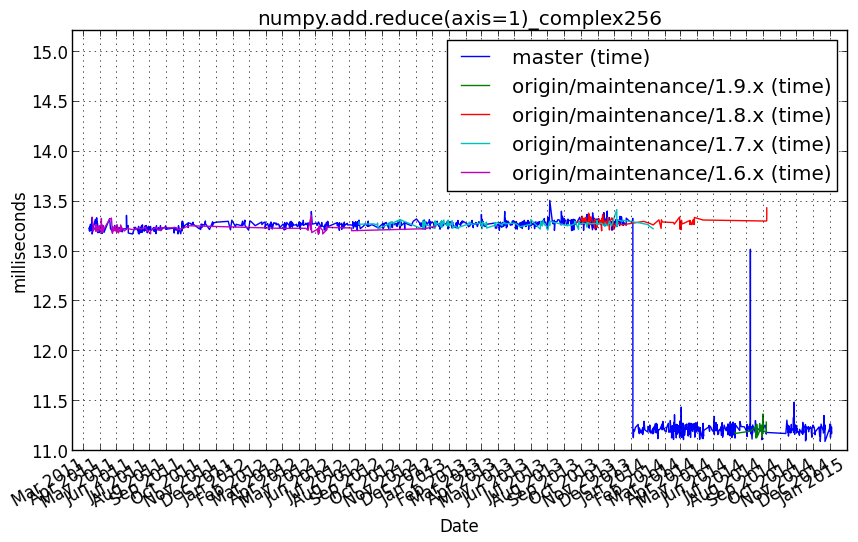
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_complex64¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['complex64']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
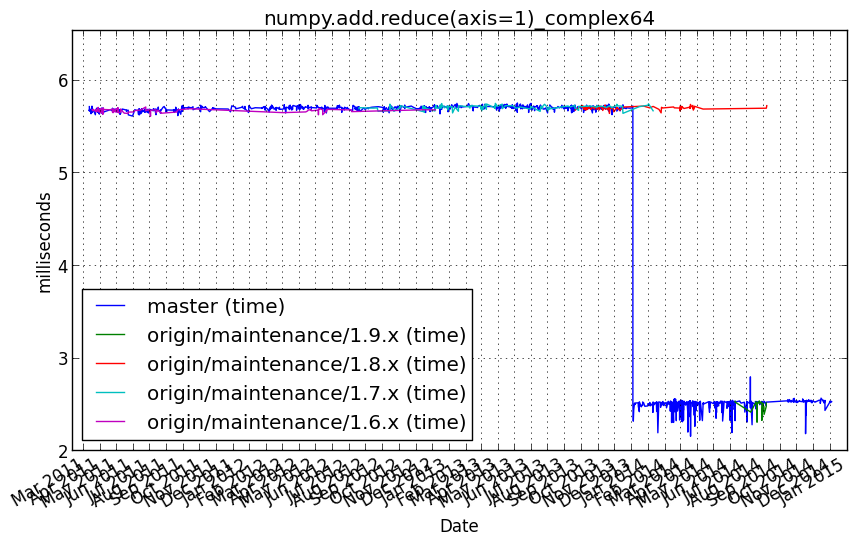
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_float16¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['float16']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
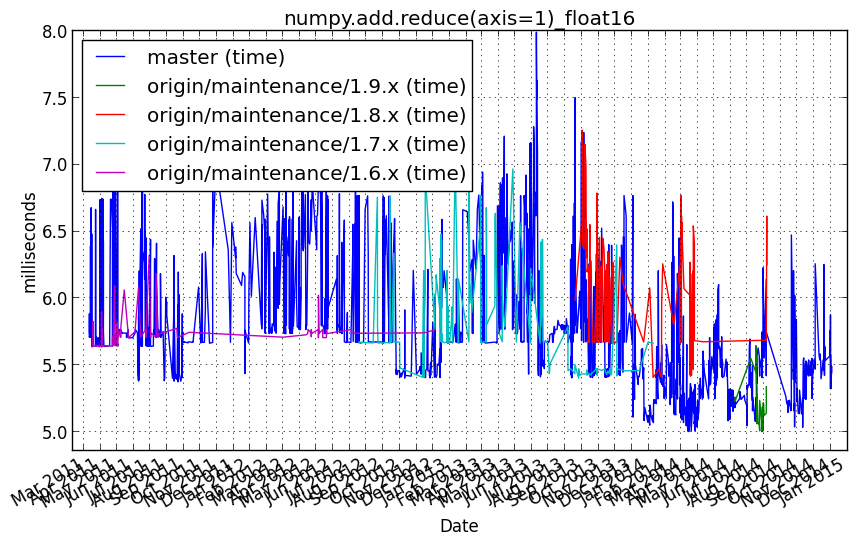
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_float32¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['float32']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
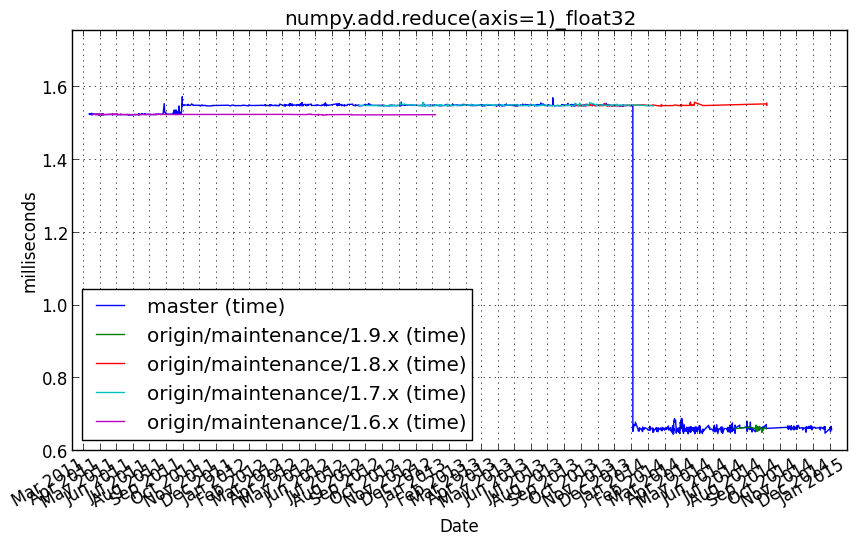
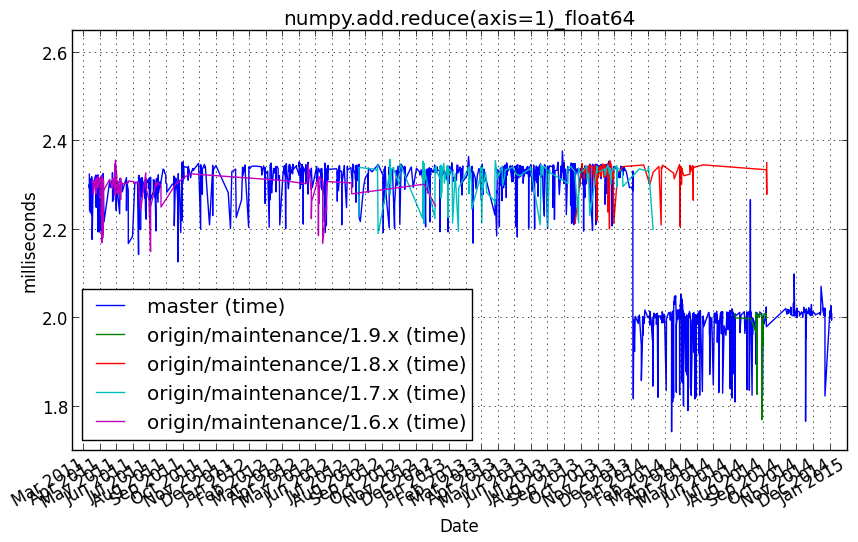
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_float64¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['float64']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
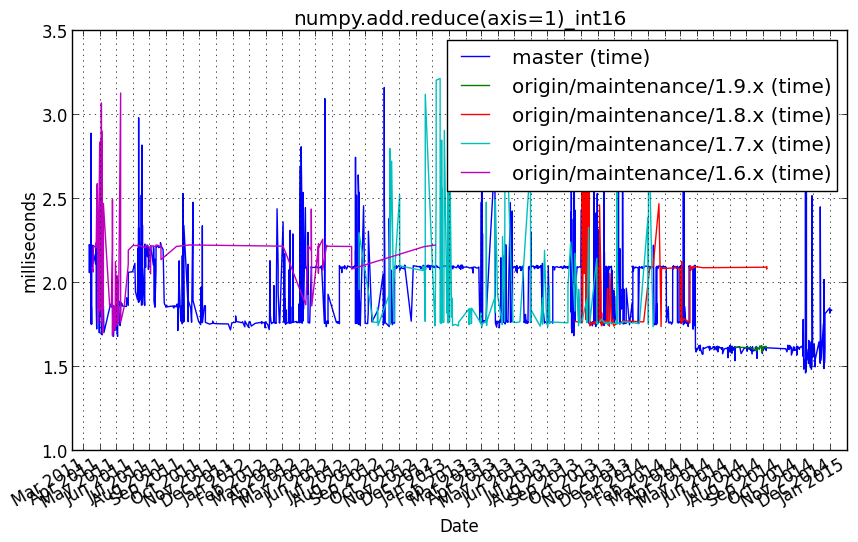
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_int16¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['int16']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
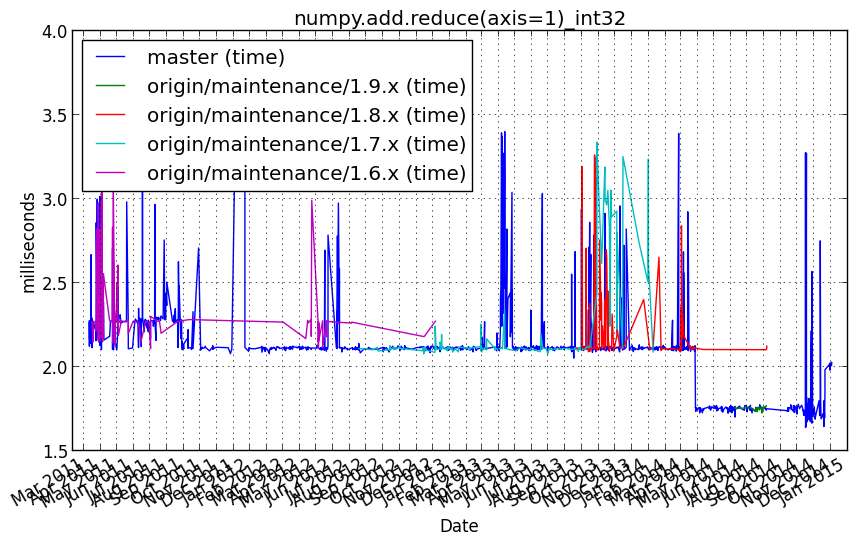
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_int32¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['int32']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
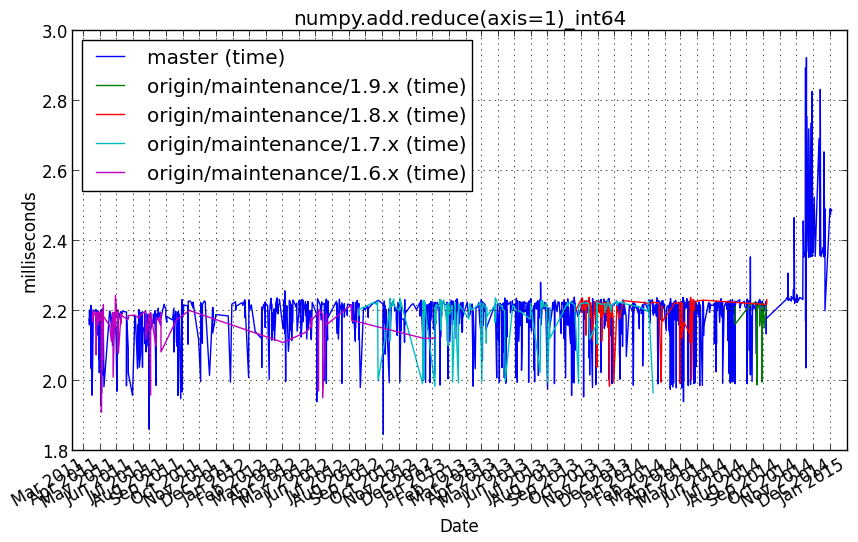
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_int64¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['int64']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
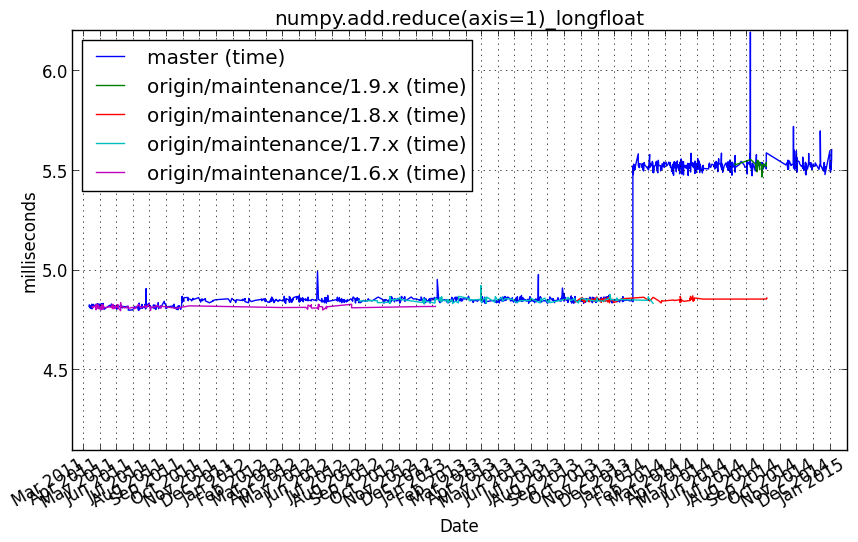
numpy.add.reduce(axis=1)_longfloat¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
a = squares['longfloat']
Benchmark statement
numpy.add.reduce(a, axis=1)
Performance graph
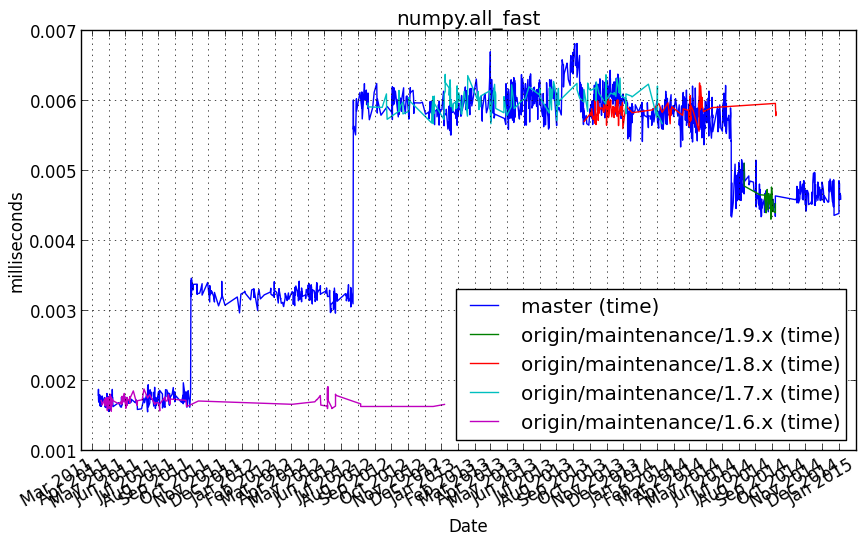
numpy.all_fast¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.zeros(100000, numpy.bool)
Benchmark statement
d.all()
Performance graph
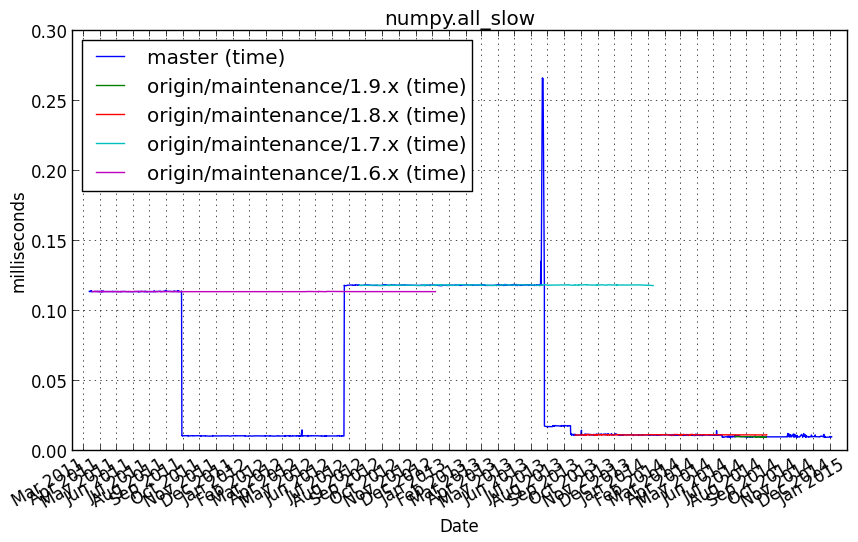
numpy.all_slow¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(100000, numpy.bool)
Benchmark statement
d.all()
Performance graph
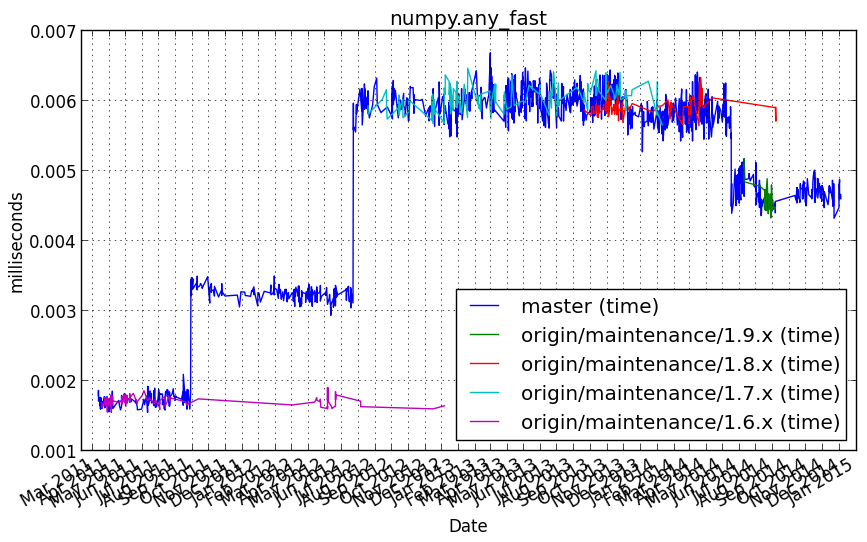
numpy.any_fast¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(100000, numpy.bool)
Benchmark statement
d.any()
Performance graph
numpy.any_slow¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.zeros(100000, numpy.bool)
Benchmark statement
d.any()
Performance graph
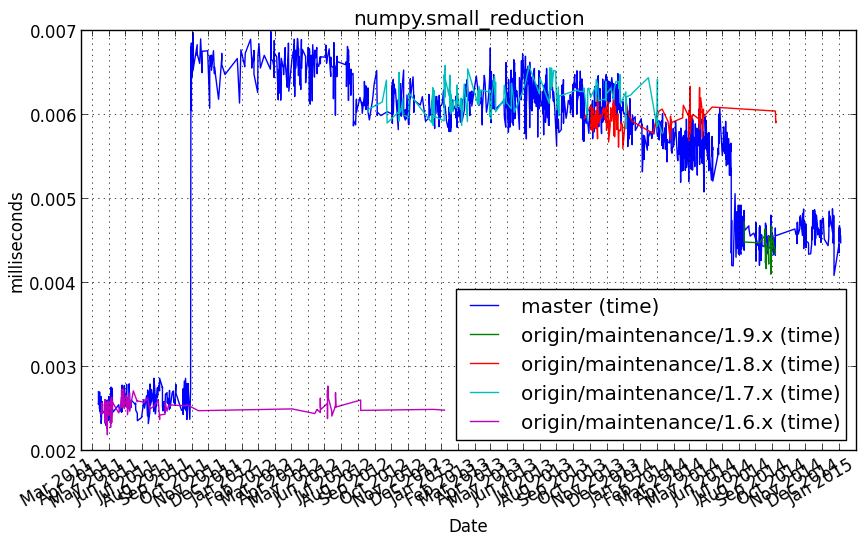
numpy.small_reduction¶
Benchmark setup
from numpy_vb_common import *
d = numpy.ones(100, dtype=numpy.float32)
Benchmark statement
numpy.sum(d)
Performance graph